Table of Content
- What is Organic Certification?
- Key Principles of Quality Management in Organic Certification
- Key notified authorities that Regulate and Authorise Certification Bodies to issue Organic Certification in India?
- Key Requirements to Obtain an Organic Certification
- Who Does Not Get Organic Certification?
- Documents Required to Obtain an Organic Certification
- Why Does Organic Certification Matter?
- Process for Obtaining Organic Certification?
- The Way Ahead
What is Organic Certification?

Organic certification is a process that ensures that the agricultural products, like food, livestock products or oilseeds, are produced without synthetic chemicals or pesticides and adhere to the specific standards. It guarantees that the farming practices are sustainable, eco-friendly, and safe for consumers.
Organisations that obtain an organic certification are allowed to label and represent their products as organic. This helps in building customers’ trust and facilitates access to new markets. Organic certification along with CE Marking and BIS certification provide an organisation with a powerful, comprehensive framework for quality assurance, legal compliance, and market expansion.
Key Principles of Quality Management in Organic Certification

Organic certification acts as an assurance for the consumer and the producer. To the consumer, it reflects that the product is safe to use, organically grown and free of any hazardous pesticides. To the producer, it helps in reflective product authenticity, building the brand’s credibility, and gaining the consumer’s trust. Apart from this, there are various principles of quality management in organic certification that make it quite important for both the consumer and producer. Some of them are:
- Compliance with Organic Standards: It ensures compliance and adherence to organic standards, including environmental sustainability, soil health, animal welfare, and prohibition of any kind of pesticides, fertilisers, or GMOs.
- Soil Health Management: It supports practices like crop rotation, composition, and cover cropping that naturally restore the soil health while prohibiting synthetic fertiliser that degrades soil structure.
- Inspection and Certification Control: It requires implementing an annual inspection process to ensure compliance with organic standards, prevent fraud, and guarantee that products are grown, handled, and processed without the use of any prohibited or hazardous input.
- Record Keeping: It mandates maintaining detailed and comprehensive records of the production, handling, and sales activity to easily verify organic management and integrity in the organisation.
- Prevention of Contamination: Organic certification requires establishing a well-established and structured product lifecycle to prevent contamination of synthetic, hazardous, and genetically modified substances.
- Biodiversity Conservation: It supports ecosystem health, food conservation, and restoration and preservation of soil health.
- Continuous Improvement: Organic certification strives for continuous improvement by establishing a system to monitor processes, analyse threats or defects, and take corrective measures for them.
- Transparency and Consumer Trust: It verifies that products meet strict, regulated standards regarding sustainable farming, eco-practices, and labelling, building transparency in processes and boosting consumers’ trust.
Key notified authorities that Regulate and Authorise Certification Bodies to issue Organic Certification in India?
| Certification Body | Details |
| National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) | NPOP is India’s official organic certification framework that sets standards for organic production, processing, and labelling. It governs accreditation of certification bodies and ensures Indian organic products comply with internationally recognised norms, supporting global trade and export of organic goods. |
| Participatory Guarantee System (PGS) | PGS is a community-based organic certification system built on trust, peer review, and farmer participation. It mainly supports small farmers and domestic markets by offering a cost-effective and locally managed certification mechanism for organic produce. |
|
Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) |
APEDA authorises and supervises accredited certification agencies under NPOP standards. These agencies inspect organic farms and processing units, conduct compliance audits, and issue certification necessary for organic product exports and large-scale commercial trade. |
Key Requirements to Obtain an Organic Certification
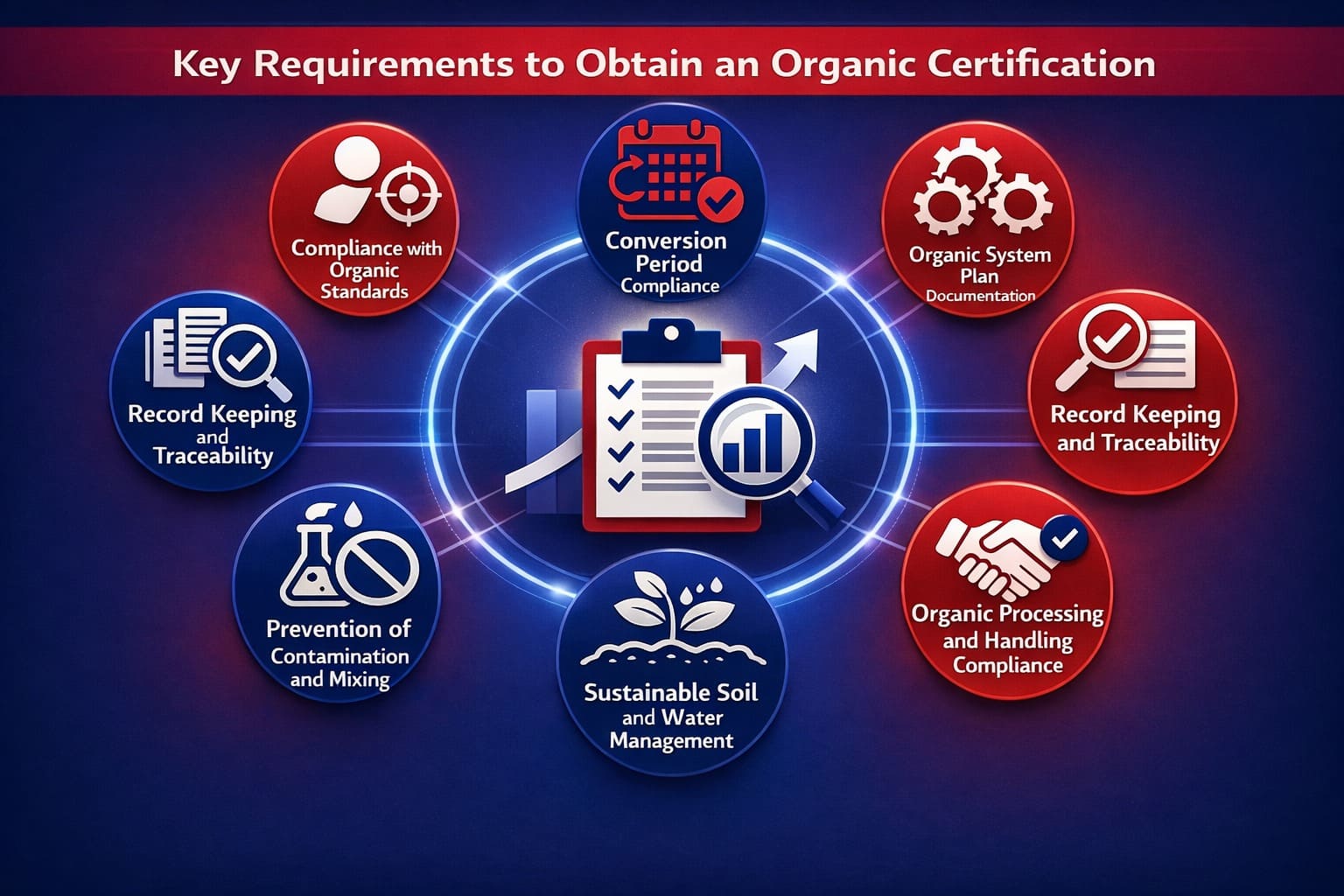
If an organisation, producer, or retailer wants to obtain organic certification, they need to fulfil the following key requirements:
1. Compliance with Organic Farming Standards: Producers must comply with all the organic farming standards, including soil and nutrient management, pest and disease control, contamination control, and input restrictions.
2. Conversion Period Compliance: Producers must observe a transition period where land follows organic practices before products can be sold as certified organic.
3. Organic System Plan Documentation: Producers must develop detailed organic system plan documentation, including a detailed description of practices, a map of all land/facilities, a list of all inputs and record-keeping systems for monitoring and tracking, ensuring no prohibited substances are used.
4. Record Keeping and Traceability: Maintain detailed production, storage, and sales records enabling traceability, verification, and quick identification of any compliance issues.
5. Prevention of Contamination and Mixing: Implement physical separation and handling controls preventing organic products from mixing or contaminating with prohibited substances during processing.
6. Sustainable Soil and Environment Management: Adopt eco-friendly farming practices, improving soil fertility, conserving water, protecting biodiversity, and reducing environmental pollution risks.
7. Organic Processing and Handling Compliance: Processing units must prevent contamination, use approved substances only, and maintain strict separation between organic and non-organic products.
8. Proper Labelling and Packaging Requirements: Products must carry accurate organic labels, certification details, and packaging ensuring product integrity without misleading or false claims.
Who Does Not Get Organic Certification?
There are certain exceptions in organic certification. It is not issued to:
1. Small-scale farmers or producer organisations with annual sales less than or equal to Rs. 12 lakhs.
2. Operations that sell directly from the farm to the end consumer.
3. Products like organic cotton, textiles, or cosmetics, which fall outside the Food Safety and Standards (Organic Foods) Regulations, 2017.
4. Products failing to meet the minimum standards of the National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) or Participatory Guarantee System (PGS-India).
5. Farms in the initial 1-3 year conversion period, unless specifically granted an exception.
Documents Required to Obtain an Organic Certification
Here is a list of documents required to obtain organic certification:
- Organic System Plan
- Farm Record and Map
- Soil and Water Test Report
- Cropping Plan
- Production and Harvest Record
- Storage and Handling Details
- Business Registration Details
Why Does Organic Certification Matter?
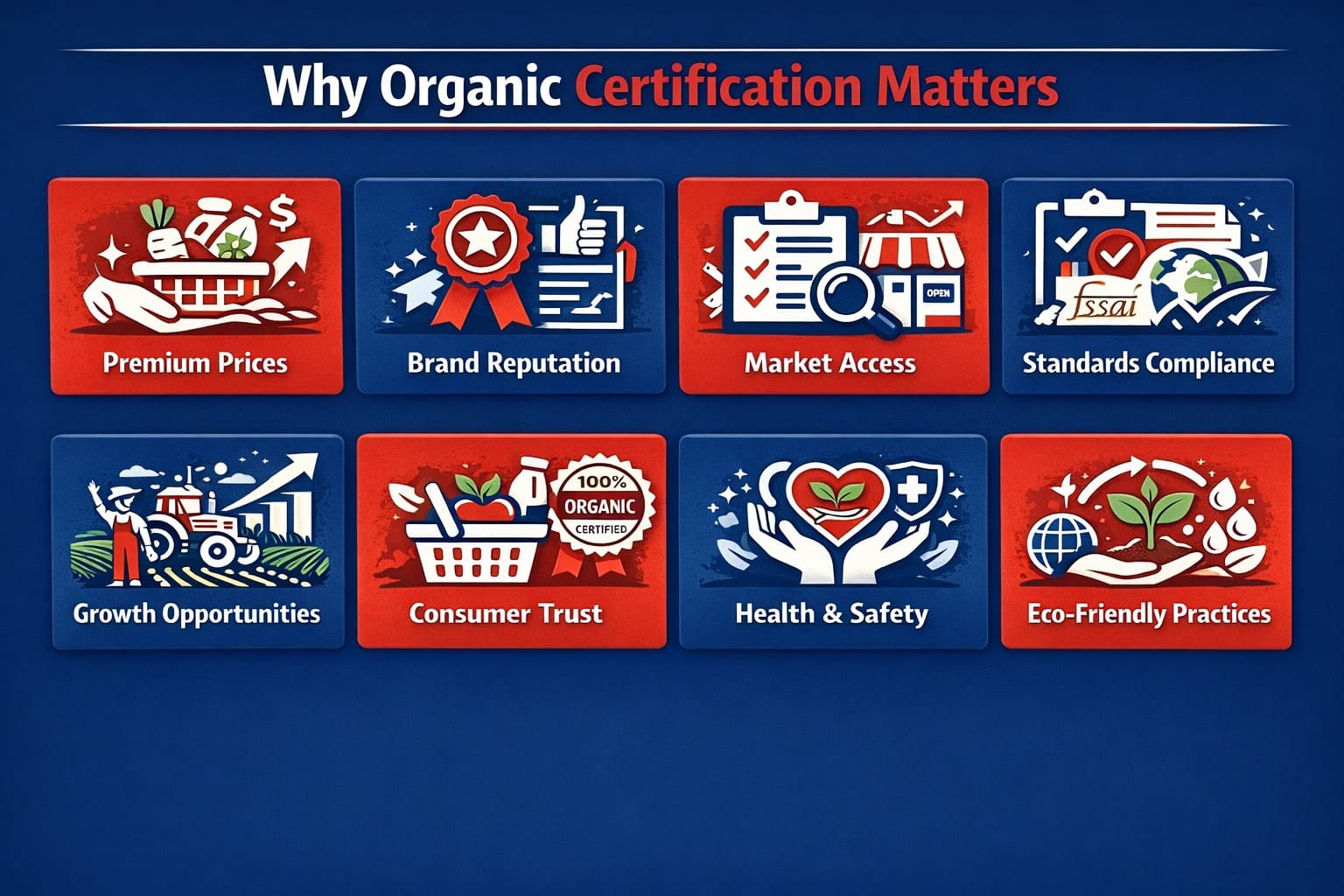
Organic certification matters a lot for the manufacturers, producers, and organisations, as well as for the consumer. With this certification, producers can charge premium prices for their products, build their brand’s reputation, easily access the market and new consumers, and accelerate their growth opportunities. This certification also helps the producers to comply with the environmental laws, food and safety standards, FSSAI regulations, and other international standards.
The certification acts as a verified guarantee for food products and enables consumers to choose the best, healthiest, and hazard-free product for them. It builds consumers’ trust in the product and confirms adherence to high standards and eco-friendly practices. Overall, organic certification promotes sustainable agriculture, protects consumer health, enhances market opportunities, and supports long-term environmental and economic benefits.
Process for Obtaining Organic Certification?
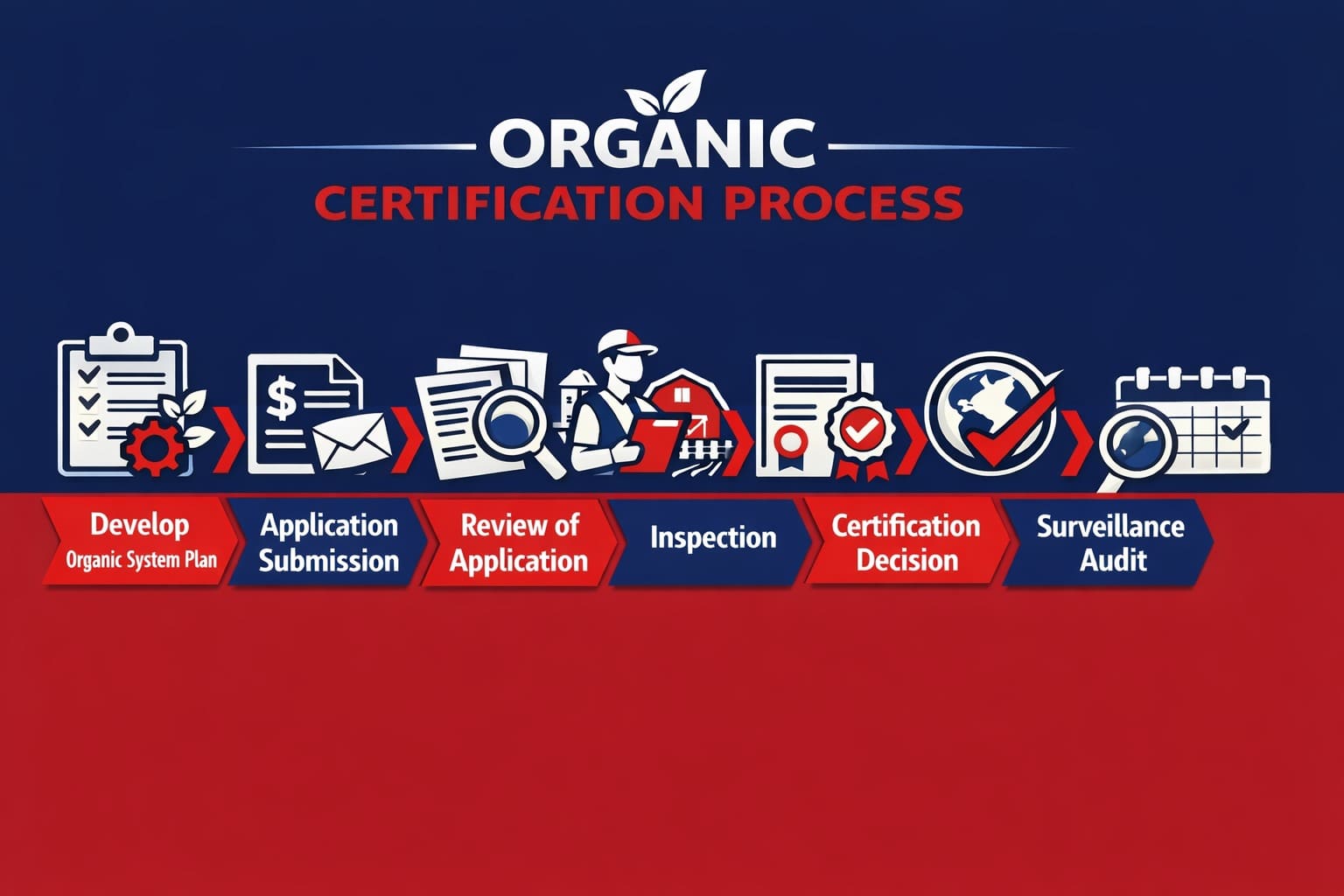
Here is the step-by-step process for obtaining organic certification:
1. Develop an Organic System Plan:
An organic system plan is a detailed document that specifies the organic process, raw material procurement, operations, roles and responsibilities. The document must be prepared by top management and should be updated regularly.
2. Application Submission
In the next step, the organisation is required to submit the application form along with all the necessary and relevant documents. The producer must mention the name of the certification body, business details, and handling system plan or organic system plan documents. The producer is required to pay the one-time fee and submit the application.
3. Review of Application
The certification body will review the application and verify the authenticity of the documents. The certification body can also ask for the production of additional documents if necessary.
4. Inspection
The certification body, after going through the application form, schedules an inspection visit. This visit is to identify the effectiveness of the organic system plan, land, facility, and processes.
5. Certification Decision
After successful inspection of the process and implementation of the plan, the certification body grants the organic certification. If any non-conformity is found during the process, the producer has to take corrective measures before obtaining the certification.
6. Surveillance Audit
To ensure the continuity of the certification, the producer or organisation has to undergo an annual surveillance audit. This audit ensures continuous improvement and conformity to the certification requirement and standards.
The Way Ahead
Organic certification is essential for ensuring product authenticity, consumer safety, and sustainable business growth. The key requirements, benefits, and process for obtaining the certification are explained above. There can be some difficulties while applying for the certification, like missing documents, non-conformities with laws and requirements or even an uneven organic system plan. To cope with these problems and simplify the application process, you can consult with us. With our professional guidance and expertise, you can obtain your organic certification without any stress or hassle.
FAQS
Have some questions about organic certification?
We have got you covered:
-
Is organic certification mandatory?
Certification becomes mandatory when producers want to legally market products using the official organic label.
- How long does organic certification take?
- What is the conversion period in organic farming?
- Which products can be organically certified?
- Can small farmers obtain organic certification?
- Does organic certification improve product value?
- What happens if organic certification standards are violated?
- Does organic certification help export businesses?
- What is residue testing in organic certification?
- Can processed food be organically certified?
- What role does soil health play in certification?
- Is packaging regulated under organic certification?
- Can organic certification be renewed?
- Are livestock products eligible for organic certification?
- Is organic certification costly?
- Can imported products be sold as organic?
- Does certification support environmental protection?
- Can retailers require organic certification?
- Why should businesses choose organic certification?
- Can organic certification apply to cosmetic products?
