MTO Insurance Essentials: Cargo Liability Coverage for 2026
- by kapil
- Updated Mar 5, 2026
- 10 mins read


As global supply chains grow more complex, Multimodal Transport Operators (MTOs) face increasing legal and financial exposure. From cargo damage and documentation errors to subcontractor risks and regulatory penalties, a single shipment today may involve multiple transport modes, jurisdictions, and stakeholders.
In 2026, cargo liability insurance for MTOs is no longer just a regulatory requirement but it is also a core risk management necessity. This guide explains the essentials of MTO insurance, with a special focus on cargo liability coverage, helping operators, freight forwarders, and logistics companies stay compliant, protected, and competitive.
Understanding MTO Insurance: A Quick Overview
Multimodal Transport Insurance is designed for entities that move goods under a single transport contract using two or more modes of transport, such as road, rail, sea, or air.
Under the Multimodal Transportation of Goods Act, 1993 (India), an MTO:
- Acts as a principal, not an agent
- Assumes responsibility for the entire transport chain
- Must have MTO registration and and insurance to obtain a license from the Director General of Shipping
This makes MTO insurance mandatory, not optional.
Why Cargo Liability Is the Core of MTO Insurance
Among all coverage sections, cargo liability is the most critical because it directly affects:
- Shippers and cargo owners
- Contractual credibility
- Financial stability of the MTO
In the event of loss, damage, delay, or misdelivery, the cargo owner’s primary claim is against the MTO, regardless of whether the loss occurred during road, sea, rail, or air movement.
What Cargo Liability Coverage Includes
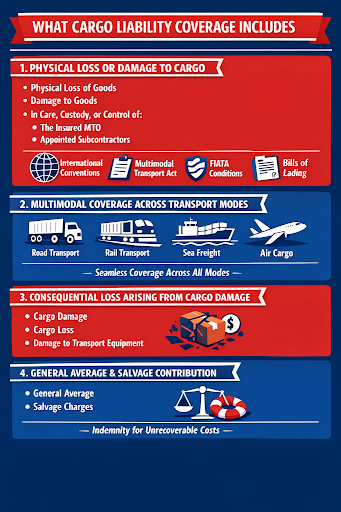
1. Physical Loss or Damage to Cargo
Cargo liability insurance covers the MTO’s legal liability for:
- Physical loss of goods
- Physical damage to goods
- Loss occurring while cargo is in the care, custody, or control of:
- The insured MTO
- Appointed subcontractors
Coverage applies when liability arises under:
- International transport conventions
- The Indian Multimodal Transport Act
- FIATA or approved standard trading conditions
- Approved bills of lading or transport documents
- Multimodal Coverage Across Transport Modes
Unlike carrier-specific policies, MTO insurance provides continuous coverage across all modes, including:
- Road transportation
- Rail transport
- Sea freight
- Air cargo
This single-policy approach eliminates coverage gaps that commonly occur when multiple standalone policies are used.
- Consequential Loss Arising From Cargo Damage
Cargo liability coverage may extend to direct consequential losses resulting from:
- Cargo damage
- Cargo loss
- Damage to transport equipment or vessels
This is particularly important for high-value or time-sensitive shipments.
- General Average and Salvage Contribution
If cargo is required to contribute to:
- General Average, or
- Salvage charges,
and the MTO is unable to recover these costs from the customer, the policy can indemnify the MTO for such unrecoverable amounts.
Errors and Omissions: A Critical Extension
In modern logistics, documentation errors can be as costly as physical damage.
The Errors and Omissions (E&O) extension covers liability arising from:
- Clerical mistakes
- Incorrect documentation
- Faulty arrangements
- Failure to follow instructions
Provided the error occurred in good faith, this cover protects MTOs against claims that do not involve physical cargo damage but still result in financial loss.
Key Cargo Liability Conditions MTOs Must Understand
Weight-Based Liability Limitation
When contractual liability terms cannot be applied, claims may be limited to:
- USD 2 per kilogram, or
- Actual loss value
(whichever is lower)
This limitation is especially relevant during:
- Road transport
- Loading and unloading
- Packing and unpacking
- Temporary storage
Subcontractor-Related Claims
If cargo loss or damage occurs while under the control of a subcontractor (such as:
- Road haulers
- Warehouse operators
- Packing agents),
the claim may be subject to:
- Special deductibles
- Sub-limits defined in the policy
MTOs are expected to:
- Appoint reputable subcontractors
- Ensure they carry adequate insurance
- Maintain rights of recovery against them
Theft and High-Risk Cargo Conditions
Theft claims are generally considered only when:
- There is forced entry, and
- Cargo is stored in a secure and locked facility
Certain high-risk cargo categories such as electronics, alcohol, jewellery, precious metals, and valuable artworks, often attract special limits and deductibles.
What Cargo Liability Does NOT Cover
Understanding exclusions is just as important as knowing coverage.
Cargo liability insurance typically excludes:
- Cash, bullion, precious stones, securities
- Livestock and perishable flowers
- Owned or leased vehicles, vessels, or aircraft
- Loss arising from fraud, dishonesty, or illegal trade
- War, terrorism, and cyber incidents
- Pollution unless sudden and accidental
- Claims arising in sanctioned or high-risk countries
These exclusions highlight the need for clear contract terms and complementary insurance solutions where required.
Claims-Made Policy: Why Timely Reporting Matters
MTO insurance operates on a claims-made basis, meaning:
- The claim must be first received during the policy period
- Notification must be given within the specified timeframe (typically 90 days)
Failure to notify on time can result in claim rejection, even if the incident occurred during the policy period.
Some policies allow an Extended Reporting Period, subject to approval and conditions.
MTO Insurance vs Carrier’s Legal Liability Policy
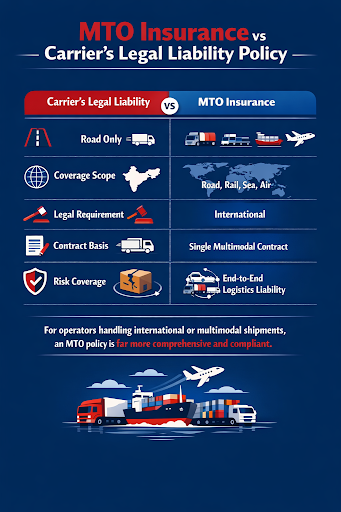
| Aspect | Carrier’s Legal Liability | MTO Insurance |
| Transport modes | Road Only | Road, rail, sea, air |
| Coverage scope | Domestic | International |
| Legal requirement | Optional | Mandatory for MTO license |
| Contract basis | Vehicle-specific | Single multimodal contract |
| Risk coverage | Limited | End-to-end logistics liability |
Why Cargo Liability Coverage Matters More in 2026
Several trends make cargo liability insurance even more critical:
- Increased cross-border trade
- Higher cargo values
- Greater reliance on subcontractors
- Stricter regulatory scrutiny
- Rising litigation and claim awareness
For MTOs, insurance is not just protection. It is proof of credibility. MTO Companies who have licence or looking to renew MTO licence should understand the importance of insurance.
Eligibility, Issuance, and Premium Structure of MTO Insurance
Understanding who can obtain MTO insurance, who issues it, and how the premium is calculated is essential for logistics businesses planning to operate as Multimodal Transport Operators. This section explains these points in a clear and practical way.
Eligibility Criteria for MTO Insurance
MTO insurance is available to entities that operate or intend to operate as Multimodal Transport Operators. To be eligible, the applicant must:
- Enter into a single multimodal transport contract covering two or more modes of transport
- Act as a principal, not merely as an agent, for the movement of goods
- Assume full responsibility for cargo from origin to final destination
- Comply with the Multimodal Transportation of Goods Act, 1993
- Apply for registration or hold a valid license issued by the Director General of Shipping
Freight forwarders, clearing and forwarding agents, shipping agents, NVOCs, and integrated logistics providers are eligible, provided they meet the above conditions.
Who Issues MTO Insurance in India
MTO insurance is issued by IRDAI-approved general insurance companies in India. These insurers offer specialised Transport and Logistics Liability policies that meet the statutory insurance requirements for MTO registration.
The issued policy is accepted by the Director General of Shipping as valid proof of insurance for licensing and renewal purposes. Insurance is granted only after a detailed review of the applicant’s operations, risk exposure, and contractual responsibilities.
How MTO Insurance Premium Is Calculated
There is no standard or fixed premium for MTO insurance. The premium is calculated based on the overall risk profile of the operator. Key factors include:
- Annual gross freight receipts
- Types of cargo handled
- Domestic and international exposure
- Modes of transport involved
- Dependence on subcontractors
- Past claims history
- Selected limits of indemnity and deductibles
Higher turnover, high-value cargo, and wider operational reach usually result in a higher premium.
Typical Premium Range for MTO Insurance
The premium for MTO insurance varies widely depending on business size and risk exposure. For small to mid-sized operators, premiums generally start from a few lakhs per annum and increase based on coverage limits and operational complexity.
Final premium amounts are determined by the insurer after reviewing the proposal form, supporting documents, and risk assessment.
Final Thoughts: Building Trust Through Proper Coverage
As supply chains become more interconnected and liability risks more complex in 2026, cargo liability coverage under an MTO insurance policy plays a crucial role in protecting Multimodal Transport Operators from financial, legal, and reputational exposure. From physical loss or damage to cargo and errors in documentation to subcontractor-related risks and regulatory obligations, a comprehensive MTO policy ensures continuity of operations and compliance with statutory requirements. More than just a licensing formality, robust cargo liability insurance strengthens trust with shippers, safeguards long-term business sustainability, and positions MTOs to operate confidently in an increasingly regulated and competitive global logistics environment.
Frequently Asked Questions on MTO Insurance
1. Is MTO cargo liability insurance mandatory in India?
Yes. Under the Multimodal Transportation of Goods Act, 1993, it is mandatory for a Multimodal Transport Operator to maintain adequate insurance coverage to obtain and retain an MTO license from the Director General of Shipping. Without valid insurance, an entity cannot legally operate as an MTO.
2. Who is eligible to get MTO insurance?
Any logistics or transport entity that operates or plans to operate as a Multimodal Transport Operator (MTO) is eligible for MTO insurance. This includes MTO companies that move cargo under a single transport contract using two or more modes of transport, such as road, rail, sea, or air. Applicants must also comply with the requirements of the Multimodal Transportation of Goods Act, 1993 and apply for registration with the Director General of Shipping.
3. Do freight forwarders and logistics companies qualify for MTO insurance?
Yes. Freight forwarders, clearing and forwarding agents, shipping agents, NVOCs, and integrated logistics providers are eligible for MTO insurance, provided they act as a principal in the transport contract and assume responsibility for the entire movement of goods, not merely as an agent.
4. Who issues MTO insurance in India?
MTO insurance is issued by IRDAI-licensed general insurance companies in India. These insurers offer specialised Transport and Logistics Liability policies, including MTO cargo liability coverage. The policy is issued only after proper risk assessment and is accepted by the Director General of Shipping for MTO licensing purposes.
5. What factors decide the premium amount for MTO insurance?
The premium for MTO insurance depends on several factors, including:
- Annual gross freight receipts
- Nature of cargo handled
- Geographic scope of operations (domestic or international)
- Modes of transport involved
- Claims history
- Use of subcontractors
- Chosen limits of indemnity and deductibles
Higher cargo values and wider operational exposure generally lead to higher premiums.
6. What is the approximate premium range for MTO insurance?
There is no fixed premium for MTO insurance. However, for small to mid-sized operators, premiums typically start from a few lakhs per year and increase based on turnover, risk profile, and coverage limits. Final pricing is determined by the insurer after reviewing the proposal and supporting documents.
7. What types of cargo losses are covered under MTO cargo liability insurance?
MTO cargo liability insurance covers the insured’s legal liability for physical loss or damage to cargo while it is in the care, custody, or control of the MTO or its appointed subcontractors. Coverage applies across all transport modes like road, rail, sea, and air, provided liability arises under applicable laws, conventions, or approved transport documents.
8. Does MTO insurance cover losses caused by subcontractors?
Yes, but with conditions. Loss or damage occurring while cargo is handled by subcontractors such as hauliers, warehouse operators, or packing agents is generally covered, subject to specific deductibles and sub-limits. MTOs are expected to appoint competent subcontractors, ensure they carry adequate insurance, and retain rights of recovery against them.
9. Are theft-related cargo claims covered under an MTO policy?
Theft claims are typically covered only if there is evidence of forced entry and the cargo was stored in a secure and locked premises or vehicle. Certain high-risk cargo categories, such as electronics, spirits, jewellery, and valuable artworks, may be subject to higher deductibles or reduced limits as specified in the policy schedule.
10. How is claim settlement affected by the claims-made nature of MTO insurance?
MTO insurance operates on a claims-made basis, meaning the claim must be first reported during the active policy period (or within an approved extended reporting period). Delayed notification, even if the incident occurred during the policy term, can lead to claim rejection, making timely reporting critical for effective coverage.



